Incentives for First-Time Homebuyers
There are a lot of programs and incentives for first-time homebuyers, but it can be hard to keep track of them all.
Each one has its own rules, limits, and fine print—which makes it easy to feel confused or overlook something valuable.
In this post, I’ll break everything down clearly so you understand exactly what’s available and make sure you’re not missing out on any savings.
What Counts as a First-Time Homebuyer?
Before getting into the incentives, it helps to know what “first-time homebuyer” means for most of these programs:
- You (or your spouse/common-law partner) haven’t owned a home that was your principal residence in the current year or in the 4 previous calendar years.
- You plan to live in the home as your principal residence.
(Provincial/local programs may have additional or slightly different requirements.)
Federal Incentives for First-Time Homebuyers
1. First Home Savings Account (FHSA)
A registered account that combines the best of an RRSP and TFSA: contributions are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for your first home (including investment growth) are tax-free.
- Annual limit: $8,000
- Lifetime limit: $40,000
- Unused annual room carries forward, so if you don’t contribute the full $8,000 in one year, you can catch up later.
- Funds must be used within 15 years of opening the account or before age 71.
Important Note: Can be stacked with the Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP).
2. Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP)
Withdraw up to $60,000 from your RRSP to buy or build a qualifying home.
- Repayment: spread over 15 years, starting the second year after withdrawal.
- Contributions don’t affect your regular RRSP deduction limit if designated as HBP repayments.
3. GST/HST New Housing Rebate (First-Time Buyers GST Rebate – New in 2025)
For new or substantially renovated homes, first-time buyers may be eligible for a full or partial rebate on GST or the federal portion of HST.
- Full rebate: Homes valued up to $1 million
- Partial rebate: Homes between $1 million–$1.5 million (phased out linearly)
- No rebate: Homes above $1.5 million
- Potential savings: up to $50,000
Important Note: The federal government has announced this program, but as of now, we don’t yet have final details on how it will work in practice. More guidance is expected.
4. 30-Year Amortization for First-Time Buyers of Insured Mortgages
As of 2025, all first-time buyers with insured mortgages (less than 20% down) may qualify for a 30-year amortization.
- Benefit: Lower monthly payments allowing for better cashflow or more purchasing power
- Trade-off: More total interest paid over time
5. Home Buyers’ Amount (First-Time Home Buyers’ Tax Credit)
A non-refundable federal tax credit to help with closing costs such as legal fees, inspections, and appraisals.
- Maximum claim: $10,000
- Value: up to $1,500 back at tax time.
Provincial Incentive – British Columbia
First-Time Home Buyers’ Program (Property Transfer Tax Exemption)
In BC, first-time homebuyers may qualify for a full or partial exemption from the Property Transfer Tax (PTT).
- What is PTT?
- 1% on the first $200,000 of fair market value (FMV)
- 2% on FMV between $200,000–$2,000,000
- 3% on FMV above $2,000,000
- Exemptions:
- Full exemption if FMV is $500,000 or less
- Partial exemption between $500,000–$835,000
- No exemption if FMV is $860,000 or more
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Canadian citizen or permanent resident
- Filed at least 2 income tax returns as a BC resident in the last 6 years
- Never previously owned a principal residence anywhere in the world
- Must move in and make the property your principal residence
This program alone can save buyers up to $8,000 on closing costs.
Real-World Example
Let’s say you’re buying a $800,000 home in BC:
- You use your FHSA savings, withdrawn tax-free.
- You withdraw $40,000 from your RRSP under the Home Buyers’ Plan.
- You save $8,000 on BC’s property transfer tax (since the home is above $500,000 but below $860,000).
- You also claim the Home Buyers’ Tax Credit = $1,500.
Total savings: Tens of thousands between rebates, exemptions, and tax advantages—bringing homeownership closer within reach.
Potential Savings – At a Glance
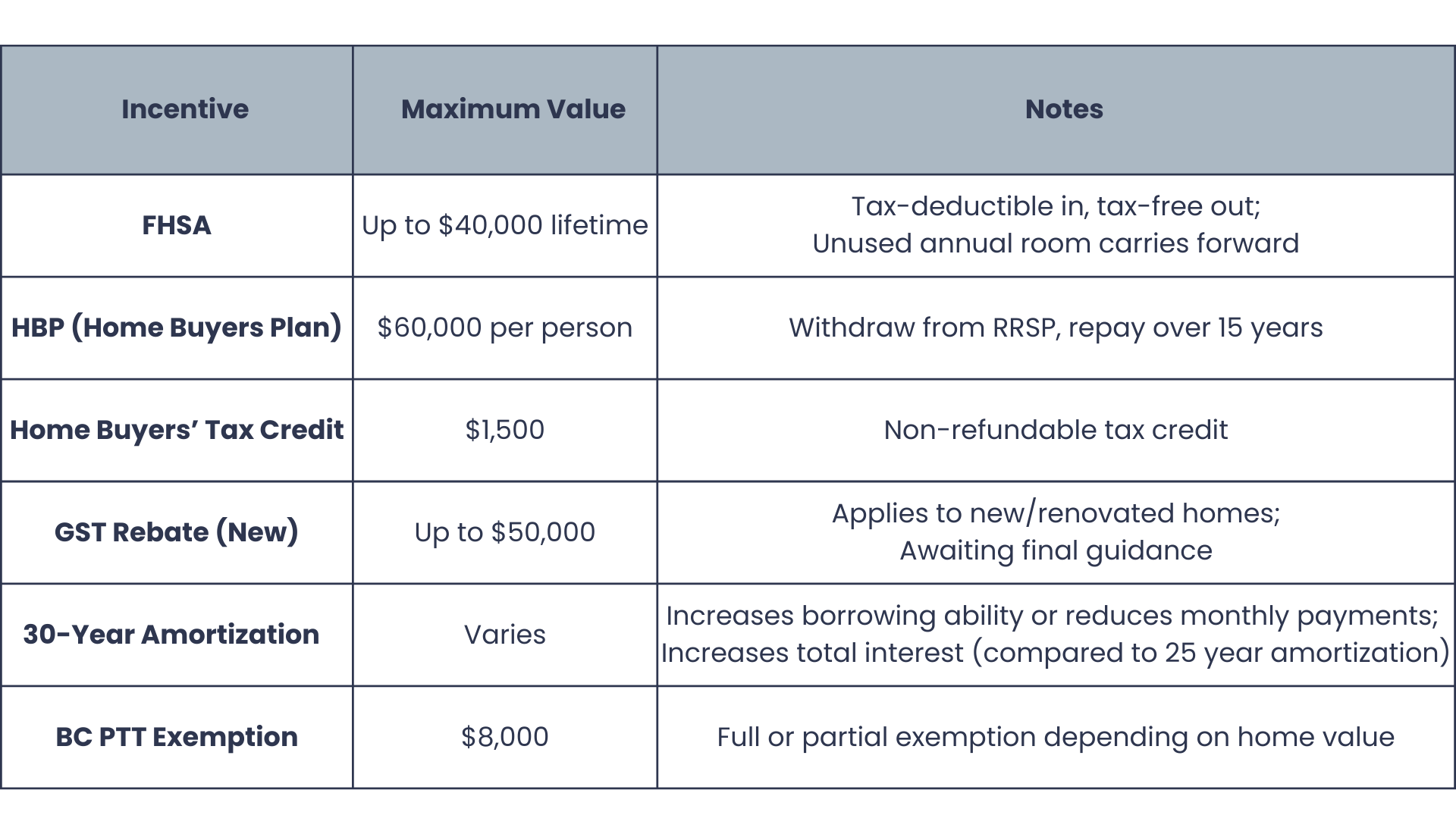
Quick Summary
- FHSA: Save up to $40,000, tax-deductible in, tax-free out
- HBP: Withdraw up to $60,000 from RRSP, repay over 15 years
- Home Buyers’ Tax Credit: Up to $1,500 tax reduction
- GST Rebate: Up to $50,000 on new builds under $1.5M (pending details)
- 30-Year Amortization: Lower monthly payments on insured mortgages for all FTHBs
- BC PTT Exemption: Up to $8,000 in tax savings
Next Steps
- Check eligibility: Federal vs BC programs differ slightly.
- Plan savings early: Use FHSA + RRSP contributions strategically.
- Run the numbers: GST rebate and PTT thresholds can make or break affordability.
- Talk with a mortgage broker: Ensure you’re combining incentives properly and not leaving money on the table.
Need help navigating these programs?
Book a consultation or call
778-988-8409.
Mortgage Term Glossary
Amortization: The total length of time to fully repay your mortgage (typically 25–30 years).
Down Payment: The upfront amount you pay toward the purchase price of a home, typically expressed as a percentage of the total price.
Equity: The difference between your home’s value and your outstanding mortgage balance.
FHSA (First Home Savings Account): A registered plan that allows tax-deductible contributions and tax-free withdrawals for your first home.
GST Rebate: A federal rebate for first-time buyers of new or substantially renovated homes, providing up to $50,000 back (pending government guidance).
HBP (Home Buyers’ Plan): A program allowing you to withdraw up to $60,000 from your RRSP for a down payment, repayable over 15 years.
Mortgage Term: The contract period for your mortgage rate and conditions (usually 1–5 years).
PTT (Property Transfer Tax): A provincial tax charged in BC when registering your home’s title; exemptions are available for first-time buyers.
RRSP (Registered Retirement Savings Plan): A registered savings plan where contributions are tax-deductible and investment growth is tax-deferred.